Kritikos Institute Discernment Model™
-
At the heart of our content is a commitment to discernment, setting us apart in a world where objectivity is often questioned and truth seems hard to grasp. Discernment, in our view, is the capacity to perceive and evaluate information with cognitive vigour and insight, enabling meaningful, impactful, and compassionate engagement with the world around. It is the skill that allows us to navigate complexities, distinguish truth from falsehood, and act with consistency, integrity, and equanimity. In today's landscape, where objectivity is frequently questioned and truth often feels elusive, we stand firm in our dedication to promoting authentic and constructive dialogue.
By assessing each piece based on its degree of logic, clarity, and other discerning factors, we ensure that our content not only informs but also inspires genuine curiosity and cognitive accountability. Our approach to discernment goes beyond mere reason and philosophical inquiry. It encompasses compassionate intent, open-mindedness, and the ability to see connections between seemingly disparate things. This holistic perspective allows us to present content that is not only intellectually rigorous but also deeply empathetic and insightful.
This approach allows us to navigate the complexities of modern discourse with integrity, fostering an environment where ideas are evaluated on their merit rather than popularity. In so doing, we empower our audience to engage in meaningful conversations that transcend the noise of biased narratives and superficial analysis.
-
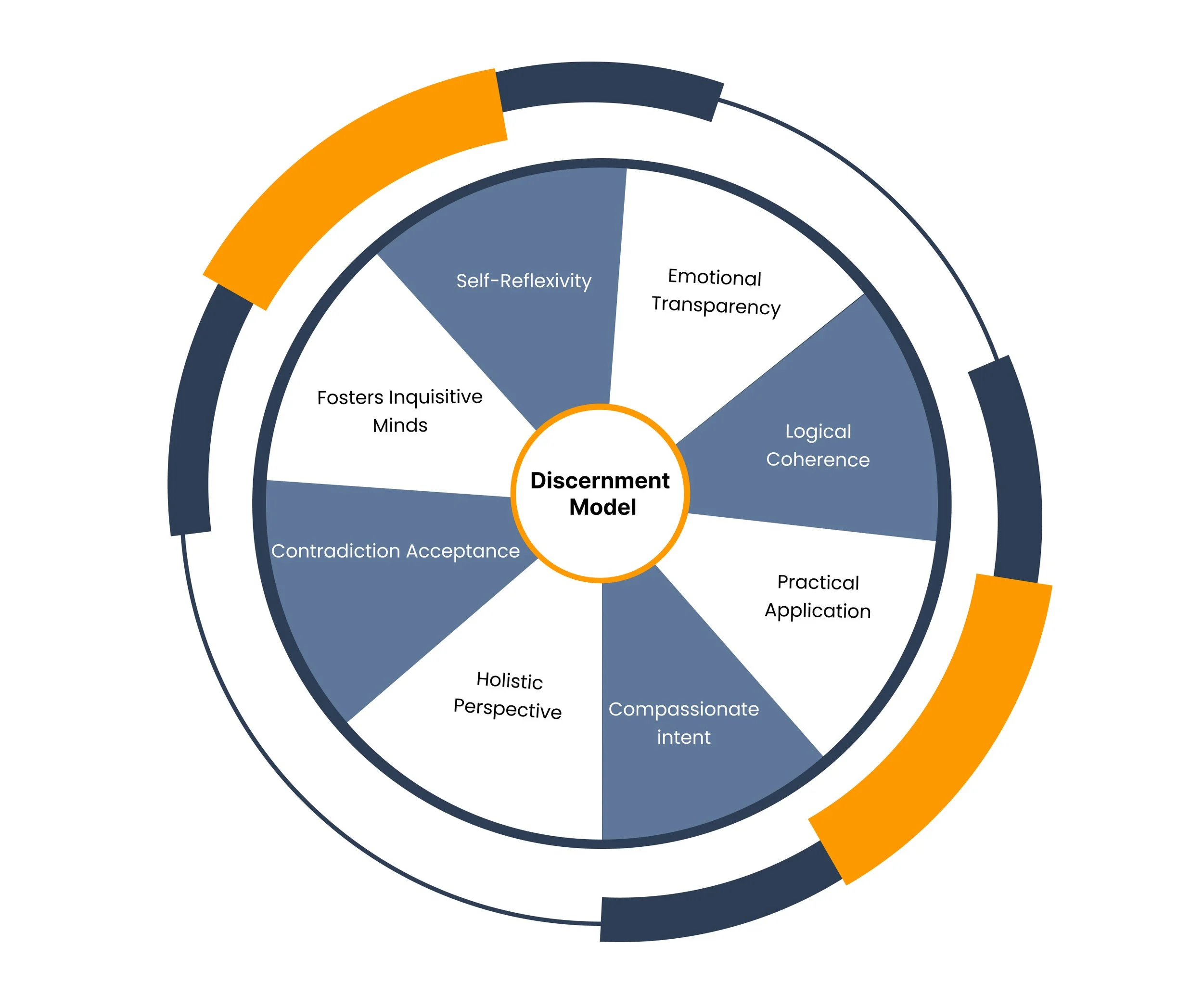
What is the Kritikos Institute Discernment Model™ ?
A minimum standard of discernment is assessed by the following characteristics:
Logical Coherence: The argument follows a logical structure leading to a coherent conclusion. Each component is grounded in fact or reasonable truth, even if that truth is not universally accepted. Conclusions drawn adhere to a coherent logic and consistent evidence, allowing the reader to see the subject from a particular, internally consistent perspective.
Emotional Transparency: The author reflects, assesses, and judges their emotional reasoning, ensuring that feelings do not cloud the discernment process but does not exclude them from it.
Self-Reflexivity: The author openly acknowledges their emotions and biases (and/or instincts and drives), recognising how these elements shape their argumentation. By understanding that their perspective emerges from interactions with others, they foster self-awareness and honesty, encouraging a more meaningful exchange of ideas that holds individuals accountable for the validity of their thinking.
Fosters Inquisitive Minds: The author encourages individuals to think independently, negating conformity and mediocrity, and fostering a deeper understanding that questions conventional wisdom and promotes genuine intellectual freedom.
Contradiction Acceptance: The author acknowledges that human life is full of contradictions, providing an alternative to the simple answers and solutions that overlook the nuances, inconsistencies, and uncertainties of life.
Holistic Perspective: The argument considers multiple dimensions of human experience, such as cognitive, emotional, and spiritual aspects, ensuring a well-rounded and integrative approach to the subject.
Compassionate Intent: The author demonstrates compassion and open-mindedness in their reasoning and judgments, considering the perspectives and lived experiences of others, even when these are incommensurable with their own.
Practical Application: The discernment process results in actionable insights and practical applications, ensuring that the reflections are not merely abstract but also relevant to real-life situations.
-
To ensure that each component of the discernment model is present and effectively assessed in the reflections, we can break down the evaluation process into clear, actionable steps.
1. Logical Coherence:· Assessment Steps:
1.1. Premise-Conclusion Check: Verify that each premise logically supports the conclusion. Ensure that the conclusion is a direct result of the premises presented.
1.2. Fallacy Detection: Identify and note any logical fallacies, such as oversimplification, blind conjecture, or distorting probabilities (Elliot Cohen, Logic-Based Therapy and Everyday Emotions, 2016).
1.3. Consistency Review: Check for consistency in reasoning throughout the piece. Ensure that the argument does not contradict itself.
2. Empirical Grounding:· Assessment Steps:
2.1. Evidence Identification: Identify all claims made and check if they are supported by empirical evidence.
2.2. Source Verification: Verify the credibility and relevance of the sources cited. Ensure that they are authoritative and up to date.
2.3. Data Accuracy: Assess the completeness and accuracy of the data presented.
3. Emotional Transparency:
· Assessment Steps:
3.1. Biased Language Check: Identify and note any biased or loaded language that could deceive the reader's perception without being transparent.
3.2. Emotional Reasoning: Check for the transparency of personal motivations, assumptions, instincts, and drives that are not supported by evidence.
3.3. Objectivity Assessment: Ensure that the argument is presented in an objective manner, focusing on facts rather than emotions. While emotional reasoning can be present, it must be transparent and explicitly acknowledged by the author. Emotional content should complement rather than contradict the factual and logical components of the argument.
4. Self-Awareness:· Assessment Steps:
4.1. Bias Acknowledgement: Check if the author acknowledges their biases, emotions and assumptions and assess the extent by which the author has engaged with other worldviews, perspectives, and ideas to arrive at their conclusions and position.
4.2. Reflective Statements: Identify reflective statements where the author discusses their perspective and how it might influence their argument.
4.3. Transparency Check: Assess the transparency of the author's methodology and the sources of their information.
5. Promoting independent thought:· Assessment Steps:
5.1. Avoidance of Dogmatic Statements: Identify whether the author avoids making absolute or dogmatic claims, instead presenting information in a way that allows for nuance and the possibility of alternative viewpoints. Assess the author's openness to different interpretations and the flexibility of their arguments.
5.2. Promoting Intellectual Engagement: Evaluate how the author actively engages the reader through a structured thought process, using logical arguments and evidence to support claims and encouraging readers to follow along and draw their own conclusions.
5.3.Diverse Perspectives: Identify instances where the author presents multiple viewpoints or perspectives on a topic, allowing readers to consider different angles and form their own conclusions.
6.Contradiction Acceptance:· Assessment Steps:
6.1.Contradiction Identification: Identify any contradictions within the argument.
6.2. Resolution Check: Ensure that the author acknowledges and/or resolves these contradictions or provides a reasonable explanation for their presence.
6.3.Nuanced Understanding: Assess whether the author demonstrates a nuanced understanding of the topic by engaging with complexities and contradictions.
6.4. Consistency Review: Check for overall consistency in the argument despite the presence of contradictions.
7. Compassionate Intent:
· Assessment Steps:
7.1. Inclusion of Mutual Perspectives: Evaluate the author's efforts to integrate various worldviews and viewpoints, encouraging non-conformity to established ideas, and intellectual curiosity and openness.7.2. Advocacy for Common Good: Evaluate if the author advocates for the common good, considering the wellbeing of society.
7.3. Avoidance of Harm: Assess the author's awareness and consideration of potential harm that their work might cause.
8. Practical Relevance:· Assessment Steps:
8.1. Actionable Insights: Identify actionable insights presented in the reflection.
8.2. Real-World Application: Assess the practical applicability of the insights to real-world situations.
8.3. Value Addition: Ensure that the argument provides value beyond theoretical discussion and offers tangible benefits.
By following these detailed assessment steps for each component, we can ensure a comprehensive review of the pieces submitted. This structured approach guarantees that all aspects of the discernment model are adequately addressed, promoting open debate, intellectual engagement, and independent thought.